Businesses these days are making significant efforts to delight their customers, and for good reasons. One of the key areas where businesses focus their efforts is in creating online self-serve applications with a great user experience in order to help customers get what they need and when they need it.
But how do businesses know if they are successful? Below are 3 key metrics that show you how to measure customer engagement.
1. Activity Time
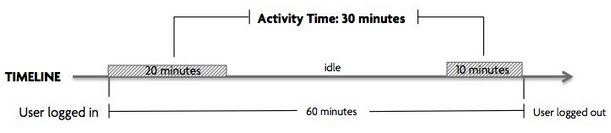
When an online service creates value, people use it and use it often. Usage is measured by the number of times a customer visits your service (sometimes termed sessions) and the elapsed time they spend in using it.
We call this Activity Time – the total time a user spends online, interacting with the offered service. Note that Activity Time measures the actual time a user spends interacting with the service, and factors out time in which the user is idle (even if logged-in). This is critical given modern usage behaviors where users typically have many web-applications and sites open on different browser tabs.
2. Visit Frequency
How often a user returns to your service is a key reflection of the value they get from it. This is often called Visit Frequency.
Visit frequency yields many potential patterns in customer behavior, as shown in the table below. The main goal is to identify the pattern that is most relevant for your service and monitor users against that pattern. If you expect a delighted user of your service to visit every day, measure against that, if you offer a seasonal service and expect them to only return on holidays, look for that pattern and so forth.
3. Core User Actions
Another indication of value customers gain is their use of Core User Actions, as defined for your service. If a user is consistently performing core actions, it is a good indication of adoption. When user’s explore new features and start to use them, the service is growing on them, and they are happy to use it more.
Conversely, if a user is not performing Core User Actions, while still spending time on the service, it may be because he is unable to get to it (indicating a usability problem) or that you don’t understand the value they are getting. Regardless, it requires further investigation to make sure the user and your offering are on track.
Core User Actions are naturally service specific, the following table gives examples of certain types of web applications and online services.
Creating a Customer Engagement Score
A combination of these core metrics: Activity Time, Visit Frequency and Core User Actions uncovers the level of user engagement for any web-application or service. To get to the combination of customer engagement metrics that is right for your particular service requires some thinking and modeling of the expected user behavior.
For the best customer success products in the industry, learn more about the Totango suite of customer engagement technology and contact sales to get started with the concepts in this article today!
 Learn which metrics other Sales Executives use:
Learn which metrics other Sales Executives use:



